A groundbreaking development in space technology has taken place, with China successfully launching a satellite equipped with a real-time Linux kernel subsystem written in the Rust programming language. This is a significant milestone in the utilization of Rust for high-performance, mission-critical systems and has the potential to revolutionize the way satellites operate in the future.
Traditionally, satellites have relied on specialized real-time operating systems (RTOSs) to handle critical tasks with strict timing constraints. These RTOSs are often proprietary and lack the flexibility and portability of Linux. The use of Rust in the Tianyi-33 satellite’s RTOS kernel offers several advantages:
- Memory Safety: Rust’s core design eliminates entire classes of memory errors at compile time, significantly improving the reliability and security of the system.
- Performance: Rust is known for its exceptional performance, making it ideal for real-time applications where every millisecond counts.
- Concurrency: Rust’s powerful concurrency features enable developers to write efficient and scalable code for multi-core processors, a crucial aspect for modern satellite systems.
- Open Source: Being open-source under the GPLv2 license, the RROS kernel allows for wider collaboration and community contributions, accelerating development and innovation.
Dual-Kernel Design for Performance and Flexibility
The Tianyi-33 satellite utilizes a dual-kernel architecture, combining the familiar Linux kernel for general-purpose tasks with the newly developed RTOS kernel written in Rust. This approach provides the best of both worlds:
- Linux Kernel: Handles routine tasks like data compression, machine learning model processing, and file management.
- RTOS Kernel: Ensures guaranteed response times for critical tasks like spatial positioning, scientific data collection, and communication.
This dual-kernel design offers several benefits:
- Flexibility: Developers can readily leverage the vast ecosystem of Linux software libraries and tools for general-purpose tasks.
- Predictability: The RTOS kernel guarantees consistent performance, eliminating jitter and ensuring reliable operation for critical functions.
- Efficiency: The separation of tasks between the two kernels allows for optimized resource utilization and power management.
About RROS Kernel
The RROS kernel brings real-time capabilities that surpass existing solutions like RT-Linux. It provides a dedicated task scheduler, synchronization mechanisms, memory allocation subsystem, and a network stack specifically designed for real-time applications. This allows the Tianyi-33 satellite to handle high-precision tasks with confidence and opens up new possibilities for future space missions.
The Kernel was developed by a research group at Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (BUPT). And they made it open source, which you can find on GitHub.
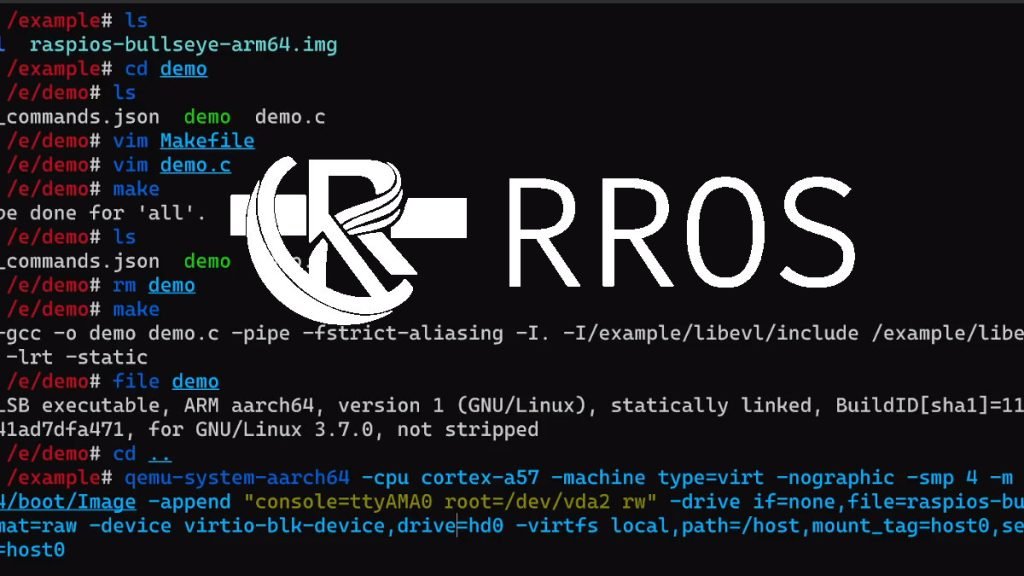
In addition, the team also provided a demo video of the Kernel in action with qemu virtual machine:
Via forum post
Recent articles from DebugPoint.com
- Cinnamon 6.6: Top New Featureson January 12, 2026
- LXQt 2.3.0: Best New Featureson January 4, 2026
- IceWM 4.0.0 Released: A Lightweight Boost for Linux Desktopson January 3, 2026
- 10 Lightweight Linux Distributions for your Old Hardware in 2026on January 3, 2026
- elementary OS 8.1: Best New Featureson January 3, 2026